Explore the International Coalition for Safe Plasma Proteins (ICSPP)
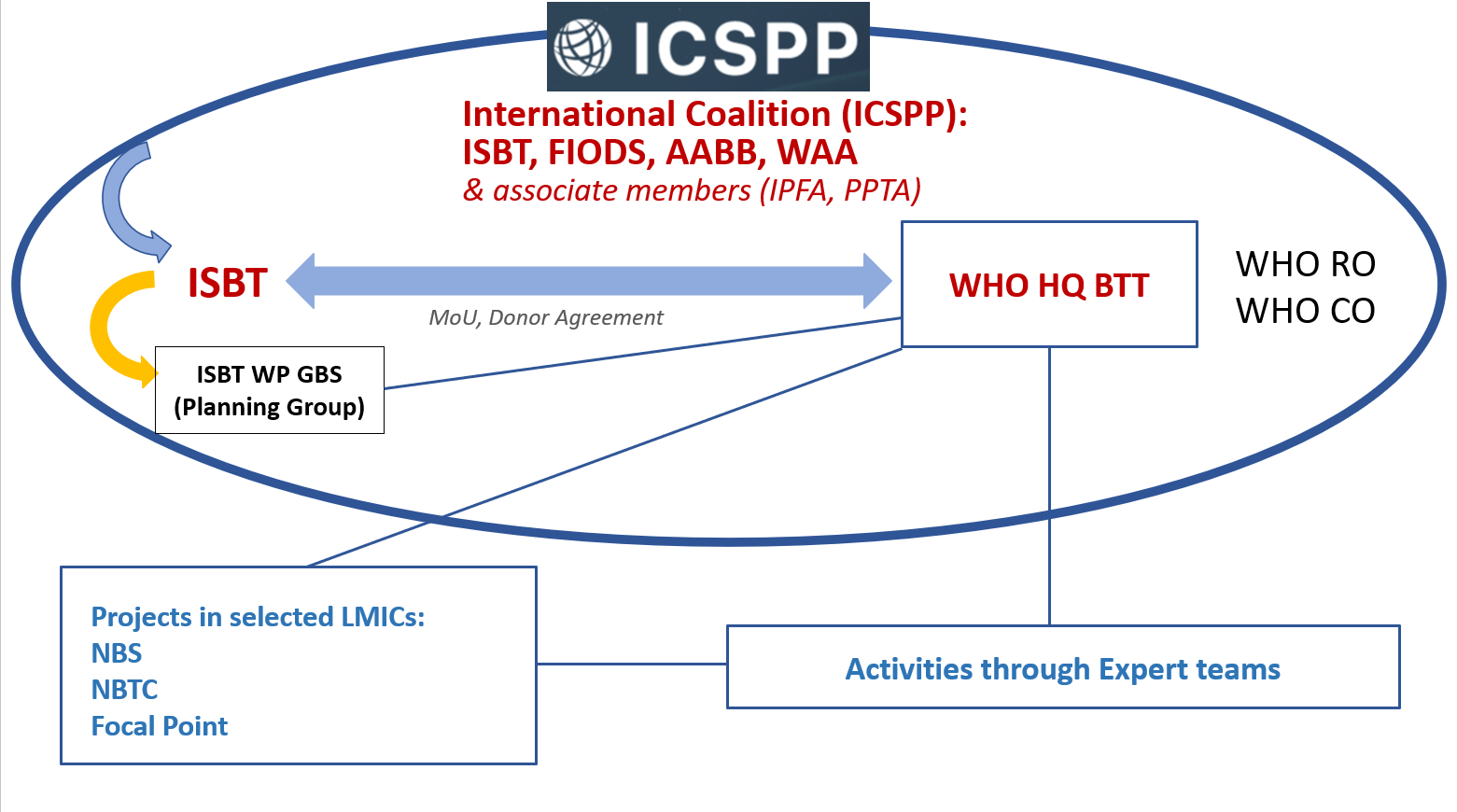
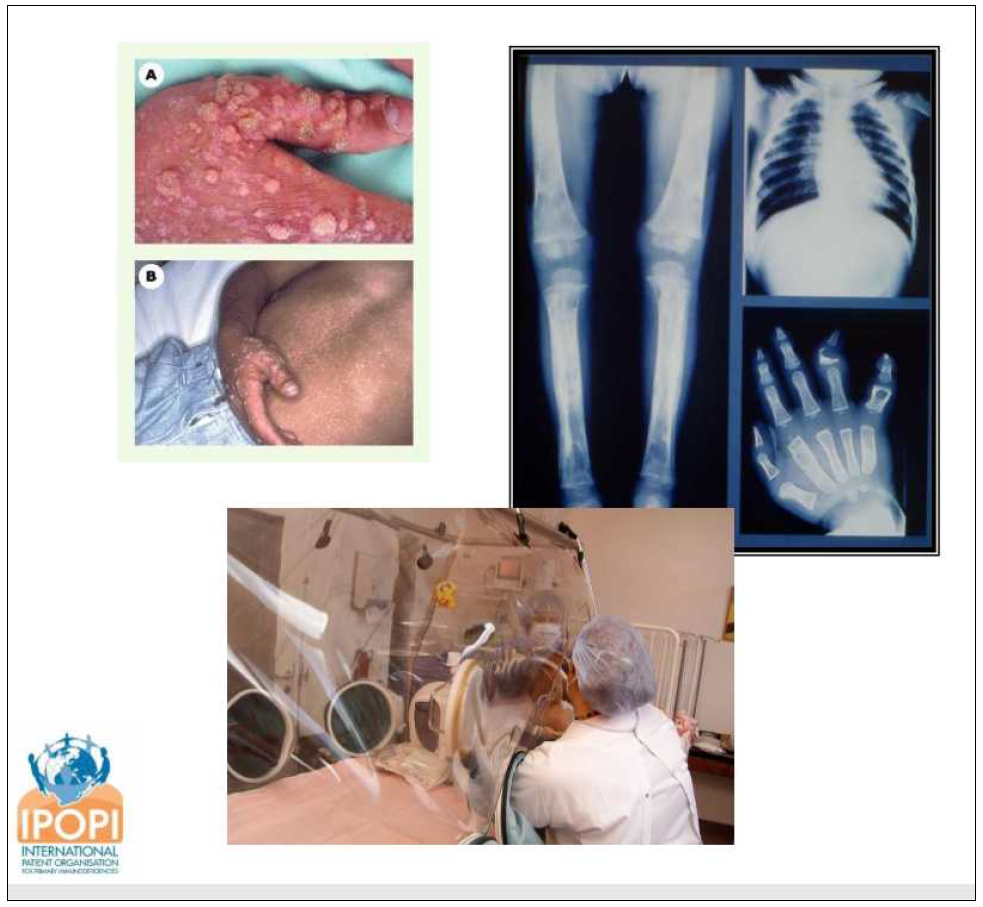
The ISBT Working Party on Global Blood Safety initiated the ICSPP as a global coalition to advance access to safe plasma proteins in Low- and Middle- Income Countries. In cooperation with the World Health Organization, this coalition was established to address the global insufficiency of plasma-derived medicinal products that are unavailable or unaffordable in many low- and middle- income countries (LMIC) and the consequent suffering and early mortality of patients with bleeding disorders, immune deficiencies, and other conditions requiring plasma-protein therapies.
Through its projects in LMIC, the ICSPP seeks to reverse the tragic wastage of domestic plasma that could be used, when meeting appropriate quality standards, either in industrial fractionation, or else, initially locally to prepare safe intermediary protein therapies.
These prominent international organizations represent major components of the blood supply chain, including blood and plasma donors, blood establishments, collection organizations, transfusion medicine specialists, and manufacturers of plasma-derived medicinal products. Additional organizations may join the ICSPP over time.
Background
History
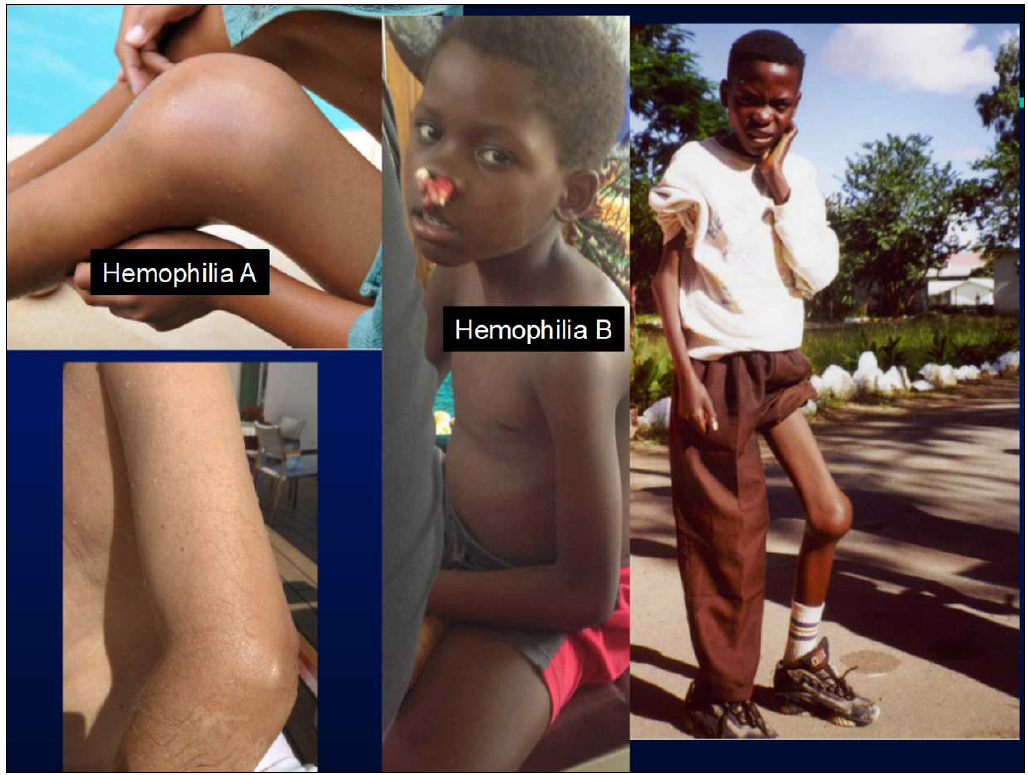
For a long time, it is well known that in most low- and middle- income countries (LMICs) supply with safe and appropriate plasma protein products is highly insufficient, almost absent - at the same time, large volumes of plasma are discarded (an estimated 9 mio. L per year in LMICs).
To solve these problems, a number of initiatives have been undertaken:
Constitution of ICSPP
Aims
- Enhancing the safety and quality as well as the availability of treatment with plasma protein products for patients in resource-constrained countries;
- Facilitating improvements in local blood establishments through alternative and innovative production approaches, allowing for reliable and increased supply with safe plasma protein products (PPPs);
- Avoiding wastage of plasma and fostering use of domestic quality-assured plasma for the manufacture of safe plasma protein products.
Goals
The International Coalition pursues several goals:
- Support introduction of new available production technologies of safe plasma protein products into low- and middle- income countries (LMICs);
- Facilitate implementation and durability / sustainability of these in LMICs;
- Empower LMIC to progressively alleviate existing supply gaps and shortages of PPPs;
Approaches
The following approaches are considered:
- Activities to strengthen elements of the national blood systems in LMICs (including Competent National Authorities with appropriate regulation, Blood Establishments, Healthcare Institutions and their hospital-based Blood Banks, Blood Donor Organisations, relevant Patient Advocacy Groups, other relevant parts);
- Local preparation in existing blood establishments of safe PPPs, using validated pathogenreduction (PR) technologies (including virus-inactivation, VI);
- Local production of safe PPPs in existing blood establishments or dedicated facilities, using validated small-scale plasma processing (purification, concentration & VI methods);
- Assistance from manufacturers of medical devices and disposables for PR/VI;
- Technology transfer from plasma fractionators;
- Contract fractionation of domestic plasma in a facility abroad;
- (National) plasma fractionation in a local facility;
- Other appropriate means to achieve the Aim and Goals of the ICSPP.
Membership
Key stakeholder organisations of the blood chain are joining the ICSPP to advance improvements in supply of safe plasma protein products in low- and middle- income countries.
The founding members of ICSPP include:
These organisations represent, at global level, blood and plasma donors, blood establishments, plasma fractionators and
patients with bleeding disorders and immunodeficiencies, acting in cooperation with the ISBT. Additional memberships in
the ICSPP can be established by unanimous agreement of the current members. The ICSPP also may grant additional
non-voting associate memberships to trade organisations that have the willingness and means to contribute to achieve the
Aim and Goals of the ICSPP (e.g., international associations of industries and manufacturers).
Modalities
A Steering Committee (SC) for the ICSPP is set up to identify, discuss and advise the ICSPP on relevant issues to achieve its Aim and Goals, consistent with “WHO Action framework to advance universal access to safe, effective and quality-assured blood
products”.
The SC is composed of all participating member organisations, each having the right to be represented in the SC by 2 individuals.
The SC is chaired by the representatives of ISBT.
The SC can invite additional individuals as observers.
The SC holds regular meetings. The frequency of meetings is according to the needs.
Decisions on all relevant issues (e.g., operating principles, projects/activities, budgets) are taken by the ICSPP, based on unanimous agreement of its voting members.
Activities
In order to achieve its Aim and reach its Goals, the ICSPP develops action plans and appropriate activities (e.g., programmes, projects, studies, publications, workshops, training events) consistent with the WHO workplan under the Achilles Project.
Activities of the ICSPP are conducted in a way to avoid any negative impact on activities or programmes of any of the member organisations and in compliance with codices of WHO.
Funding
Funds to achieve the Aim and Goals of the ICSPP are of multiple origin, abiding the rules and regulations of the members of the ICSPP and of WHO. Funds contributed to the ICSPP by commercial entities or their associations must be donated without conditions.
The budget of the ICSPP is coordinated by ISBT. Subject to establishment of a donor agreement, ISBT will transfer funds raised by the ICSPP to WHO for its use to implement agreed activities.
Responsibilities and liabilities of the cooperating parties
- ISBT serves as a host for the ICSPP by convening periodic meetings, chairing the Steering Committee (SC), managing the budget, keeping records of decisions and actions of the ICSPP. As able, ISBT may engage in fundraising for activities of the ICSPP. On a regular periodic basis, ISBT members on the SC inform the ISBT Board about progress of the ICSPP.
- As full members of the ICSPP, the stakeholder organizations carry out activities as agreed by unanimous agreement of the SC. The stakeholder organizations self-fund their participation in the ICSPP. As able, the stakeholder organizations may engage in fundraising for activities of the ICSPP.
- Associate members of the ICSPP engage in activities according to their agreements with the SC.
N.B. 2. ICSPP has established closed cooperation with WHO BTT through signed Memorandum of Understanding (MoU)
and Donor Agreement (DA).
Pilot Projects
Resources